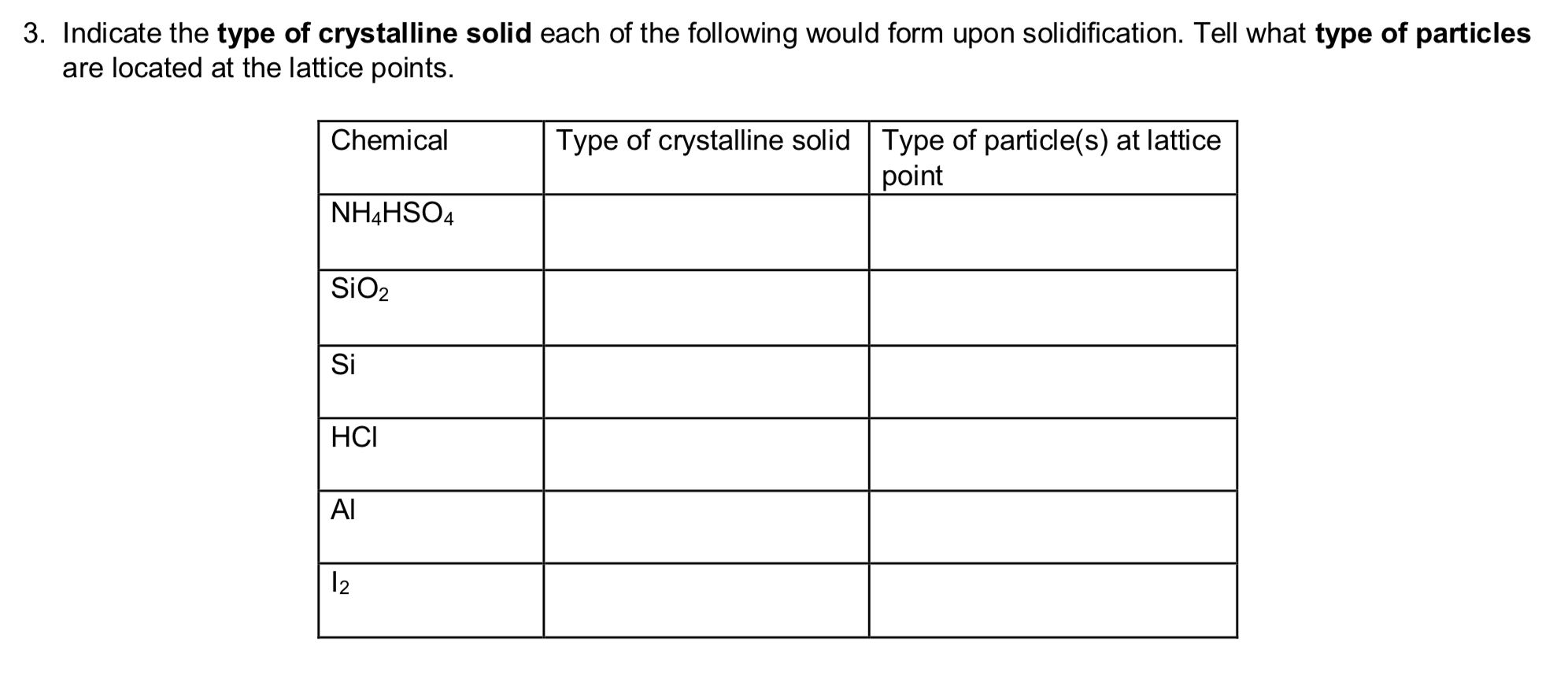
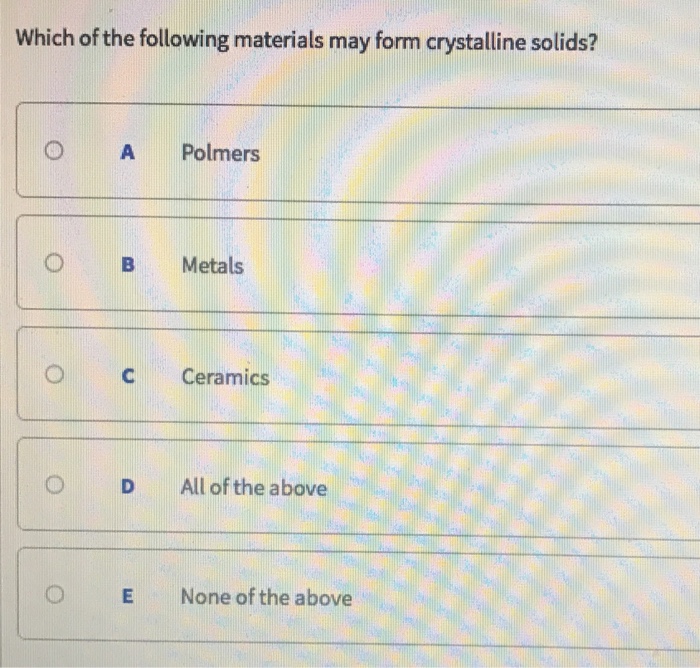
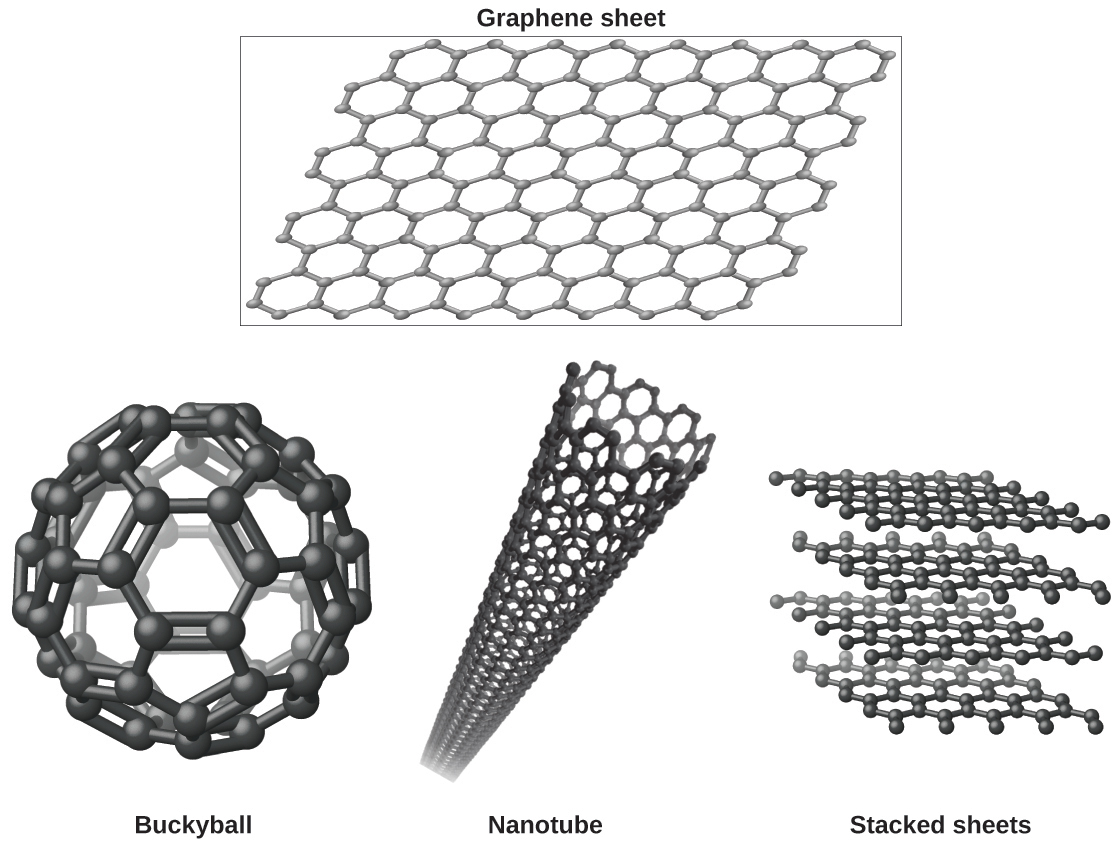
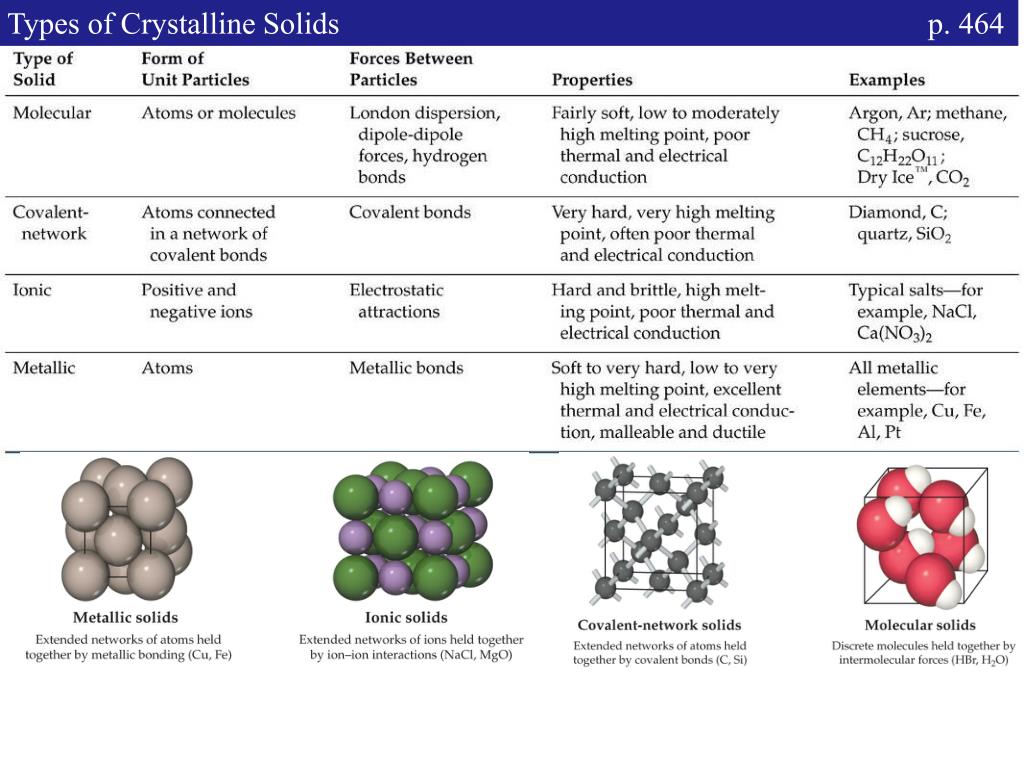
Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids
Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids - Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Which of the following materials may form crystalline. Web metals, ceramics, and polymers. Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above; Web polymorphism is the occurrence of multiple crystalline forms of a material. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Based on the intermolecular forces acting between them, the crystalline solids can be further classified. Processing, structure, properties, and performance. Polymers, metals, ceramics for the (fcc). Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate r at which e is a minimum.
These solids are classified into four types on the basis of the nature of bonding present in their constituent particles. Which of the following materials may form crystalline solids?* 5 (2 points) none of the above ceramic polymers metals 27 composites show transcribed image. Platinum, silver, copper, zinc, etc. Web polymorphism is the occurrence of multiple crystalline forms of a material. The key components of materials science and engineering include? It is found in many crystalline materials including polymers, minerals, and metals. Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of. Polymers, metals, ceramics for the (fcc). Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature.
The structure of metallic crystals is. Web classes of crystalline solids. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of. Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above; Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate e₀. Which of the following materials may form crystalline. The key components of materials science and engineering include? Inorganic salts like sodium chloride, magnesium sulphate, potassium bromide,. Web 13 rows classes of crystalline solids.
The Solid State of Matter · Chemistry
Processing, structure, properties, and performance. Which of the following materials may form crystalline. These solids are classified into four types on the basis of the nature of bonding present in their constituent particles. Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Web classes of crystalline solids.
Solved 3. a. Name the five types of crystalline solids. i)
Web metallic solids like gold. Polymers, metals, ceramics for the (fcc). Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? The key components of materials science and engineering include?
CLASSIFICATION OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS YouTube
Platinum, silver, copper, zinc, etc. The key components of materials science and engineering include? Web which of the following materials may form crystalline solids? Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate r at which e is a minimum. Processing, structure, properties, and performance.
11.7 Structure of Solids Chemistry LibreTexts
Inorganic salts like sodium chloride, magnesium sulphate, potassium bromide,. The structure of metallic crystals is. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the. Web metals, ceramics, and polymers. Which of the following materials may form crystalline.
Solved Which of the following materials may form crystalline
Web you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Platinum, silver, copper, zinc, etc. These solids are classified into four types on the basis of the nature of bonding present in their constituent particles. Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the.
Types of Solids (M11Q3) UWMadison Chemistry 103/104 Resource Book
Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Metallic solids metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms [link]. Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Web metallic solids like gold. Web classes of crystalline solids.
Which of the Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids Marahas
Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate e₀. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the. Web polymorphism is the occurrence of multiple crystalline forms of a material. Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Processing, structure, properties, and performance.
11.12 Crystalline Solids The Fundamental Types YouTube
Web classification of crystalline solids. Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Web metals, ceramics, and polymers. Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate r at which e is a minimum.
PPT Crystalline Solids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Web sodium chloride is an ionic solid. Web when an element exist in more than one crystalline form, this is called allotropy and crystalline forms are called allotropes or allotropic forms. Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? Which of the following materials may form.
Show the structure of crystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous
Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the. Web polymorphism is the occurrence of multiple crystalline forms of a material. Which of the following materials may form crystalline. Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above; Processing, structure, properties, and performance.
Web Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids?
Polymers, metals, ceramics, all of the above all of the above; Processing, structure, properties, and performance. Given the following potential with ea=0.5/r⁶ and er=32/r¹², calculate r at which e is a minimum. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of.
Web Metallic Solids Like Gold.
Web sodium chloride is an ionic solid. Web polymorphism is the occurrence of multiple crystalline forms of a material. Metallic solids metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms [link]. Web classes of crystalline solids.
The Structure Of Metallic Crystals Is.
Polymers, metals, ceramics for the (fcc). Based on the intermolecular forces acting between them, the crystalline solids can be further classified. Web most solid substances are crystalline in nature. Web 13 rows classes of crystalline solids.
Web Which Of The Following Materials May Form Crystalline Solids?
Ceramics, polymers, and metals what is the difference between atomic structure and crystal structure? These solids are classified into four types on the basis of the nature of bonding present in their constituent particles. Web classification of crystalline solids. Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the.