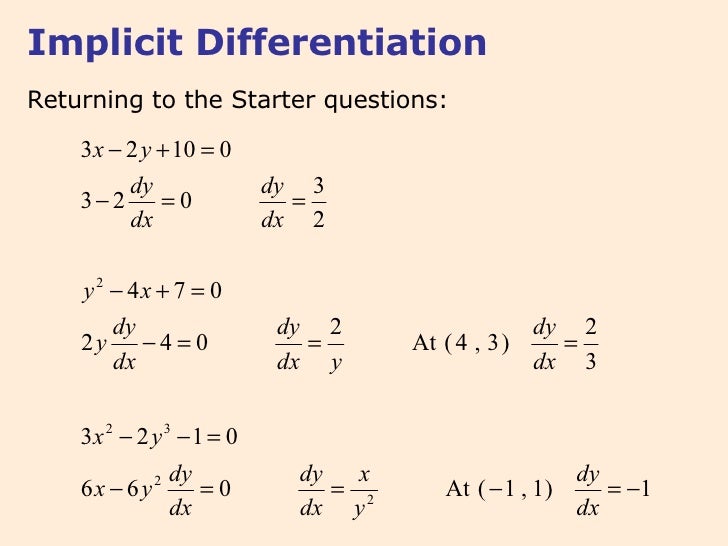
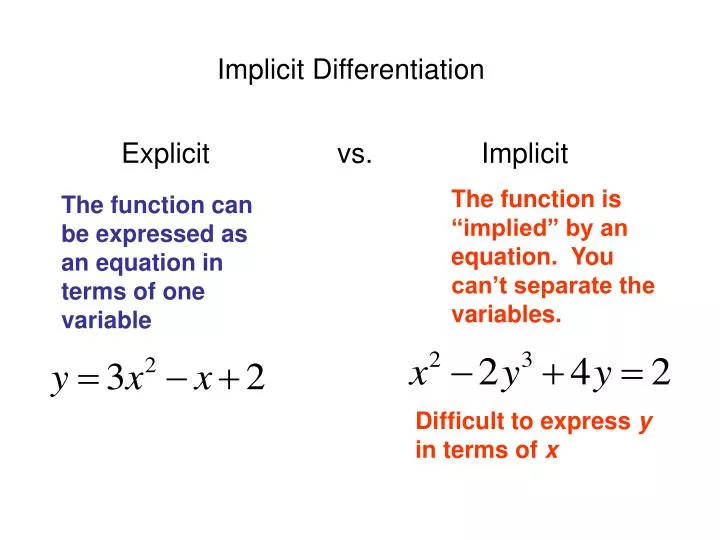
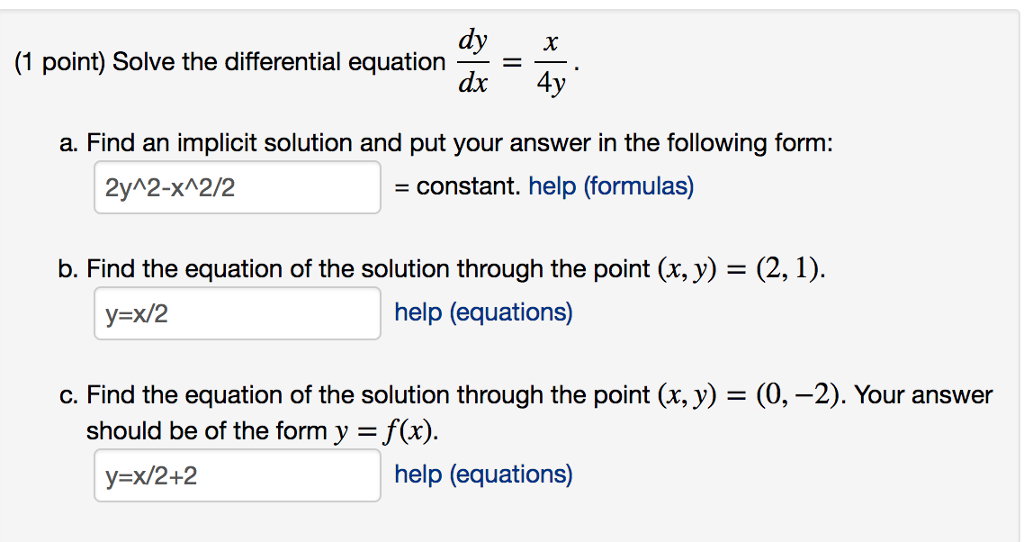
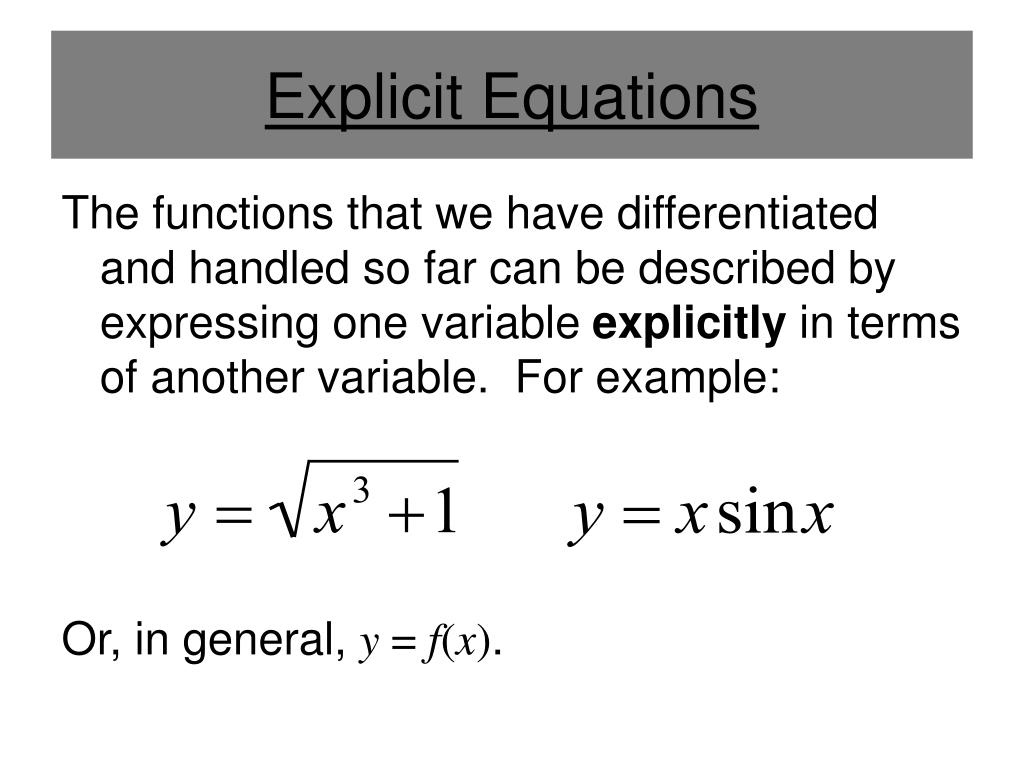
Implicit Form Differential Equation
Implicit Form Differential Equation - Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. In most discussions of math, if the dependent variable y is a function of the independent variable x, we express y in terms of x. The other answer has more detail — but to put it more simply, an explicit solution gives us our dependent variable as a function of our independent variable. Web to this point we’ve done quite a few derivatives, but they have all been derivatives of functions of the form y = f (x) y = f ( x). Questions tips & thanks want to join the conversation? D/dx becomes an algebraic operation like sin or square root, and can perform it on both sides of an equation. In applications, the functions generally represent physical. Web in mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. Separating differential equations into x and y parts is fine;
Web the implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Web given an implicit equation in x and y, finding the expression for the second derivative of y with respect to x. Web to this point we’ve done quite a few derivatives, but they have all been derivatives of functions of the form y = f (x) y = f ( x). For example, the implicit equation of the unit. Separating differential equations into x and y parts is fine; Web implicit differentiation is a way of differentiating when you have a function in terms of both x and y. If this is the case, we say that y. To perform implicit differentiation on an equation that defines a function \(y\) implicitly in terms of a variable \(x\), use the. Web implicit differential equation of type \(y = f\left( {x,y'} \right).\) here we consider a similar case, when the variable \(y\) is an explicit function of \(x\) and \(y'.\) introduce the.
Yet sometimes you just can't come up with a neat y. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. If this is the case, we say that y. There are two ways to define functions, implicitly and explicitly. In applications, the functions generally represent physical. Web given an implicit equation in x and y, finding the expression for the second derivative of y with respect to x. D/dx becomes an algebraic operation like sin or square root, and can perform it on both sides of an equation. Separating differential equations into x and y parts is fine; Web implicit differential equation of type \(y = f\left( {x,y'} \right).\) here we consider a similar case, when the variable \(y\) is an explicit function of \(x\) and \(y'.\) introduce the. There is one differential equation that.
How to solve implicit differential equation? Mathematics Stack Exchange
For example, according to the. Web answer (1 of 3): Web in mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. There are two ways to define functions, implicitly and explicitly. In most discussions of math, if the dependent variable y is a function of the independent variable x, we express y.
Differential Equations Explicit Solution YouTube
Web implicit differentiation is a way of differentiating when you have a function in terms of both x and y. Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. The other answer has more detail — but to put it more simply, an explicit solution gives us our dependent variable as a function.
Core 4 Implicit Differentiation 1
Questions tips & thanks want to join the conversation? There is one differential equation that. This is the formula for a circle with a centre at (0,0) and. Web the implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; D/dx becomes an algebraic operation like sin or square root, and can perform it on both sides of an equation.
PPT Implicit Differentiation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
If this is the case, we say that y. Web to find the implicit derivative, take the derivative of both sides of the equation with respect to the independent variable then solve for the derivative of the dependent variable with. To perform implicit differentiation on an equation that defines a function \(y\) implicitly in terms of a variable \(x\), use.
Calculus Implicit Differentiation YouTube
In most discussions of math, if the dependent variable y is a function of the independent variable x, we express y in terms of x. For example, according to the. Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. This is done using the chain rule, and viewing y as an implicit function.
Solved (1 point) Solve the differential equation
Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. For example, according to the. Web with implicit differentiation, you're transforming expressions. The other answer has more detail — but to put it more simply, an explicit solution gives us our dependent variable as a function of our independent variable. In applications, the functions.
PPT Section 2.5 Implicit Differentiation PowerPoint Presentation
Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. Web to find the implicit derivative, take the derivative of both sides of the equation with respect to the independent variable then solve for the derivative of the dependent variable with. This is the formula for a circle with a centre at (0,0) and..
Differential Equations (Part 2 Implicit Differentiation) YouTube
Web in mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. Web with implicit differentiation, you're transforming expressions. In most discussions of math, if the dependent variable y is a function of the independent variable x,.
Solved Write The Equation In The Form Then Use The Substi...
For example, according to the. If this is the case, we say that y. The other answer has more detail — but to put it more simply, an explicit solution gives us our dependent variable as a function of our independent variable. Separating differential equations into x and y parts is fine; Web to this point we’ve done quite a.
3.2 implicit equations and implicit differentiation
For example, the implicit equation of the unit. Web the implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Web in mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. D/dx becomes an algebraic operation like sin or square root, and can perform it on both sides of an equation. Web implicit differential.
Questions Tips & Thanks Want To Join The Conversation?
Unfortunately, not all the functions. Web given an implicit equation in x and y, finding the expression for the second derivative of y with respect to x. Web implicit differentiation is a way of differentiating when you have a function in terms of both x and y. Web implicit differential equation of type \(y = f\left( {x,y'} \right).\) here we consider a similar case, when the variable \(y\) is an explicit function of \(x\) and \(y'.\) introduce the.
Web The Implicit Solution Of This Differential Equation Is $X^2+Y(X)^2=R^2$;
This is the formula for a circle with a centre at (0,0) and. Web answer (1 of 3): Web to this point we’ve done quite a few derivatives, but they have all been derivatives of functions of the form y = f (x) y = f ( x). In applications, the functions generally represent physical.
If This Is The Case, We Say That Y.
It can also be quite helpful. D/dx becomes an algebraic operation like sin or square root, and can perform it on both sides of an equation. This is done using the chain rule, and viewing y as an implicit function of x. In most discussions of math, if the dependent variable y is a function of the independent variable x, we express y in terms of x.
Web To Find The Implicit Derivative, Take The Derivative Of Both Sides Of The Equation With Respect To The Independent Variable Then Solve For The Derivative Of The Dependent Variable With.
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Web a differential equation is any equation which contains derivatives, either ordinary derivatives or partial derivatives. Web with implicit differentiation, you're transforming expressions. Web up to 5% cash back finding implicit solutions.