Why Do Atoms Form Chemical Bonds
Why Do Atoms Form Chemical Bonds - When atoms approach one another, their electrons interact and tend to distribute themselves in space so that the total energy is lower than it would be in any alternative arrangement. Web posted by city chemical on monday, 01 april 2019. Web why do atoms bond? But why do atoms bond to each other in this way? Simply put, atoms form bonds in order to become more stable. There are three different types of chemical bonds:. All bonds appear to link atoms through a sharing of — or an attempt to share — electrons. Web a chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules, crystals, and other structures. According to the types of bonds contained in a molecule, the physical properties including melting point, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity and solubility are determined. Web why do atoms form chemical bonds?
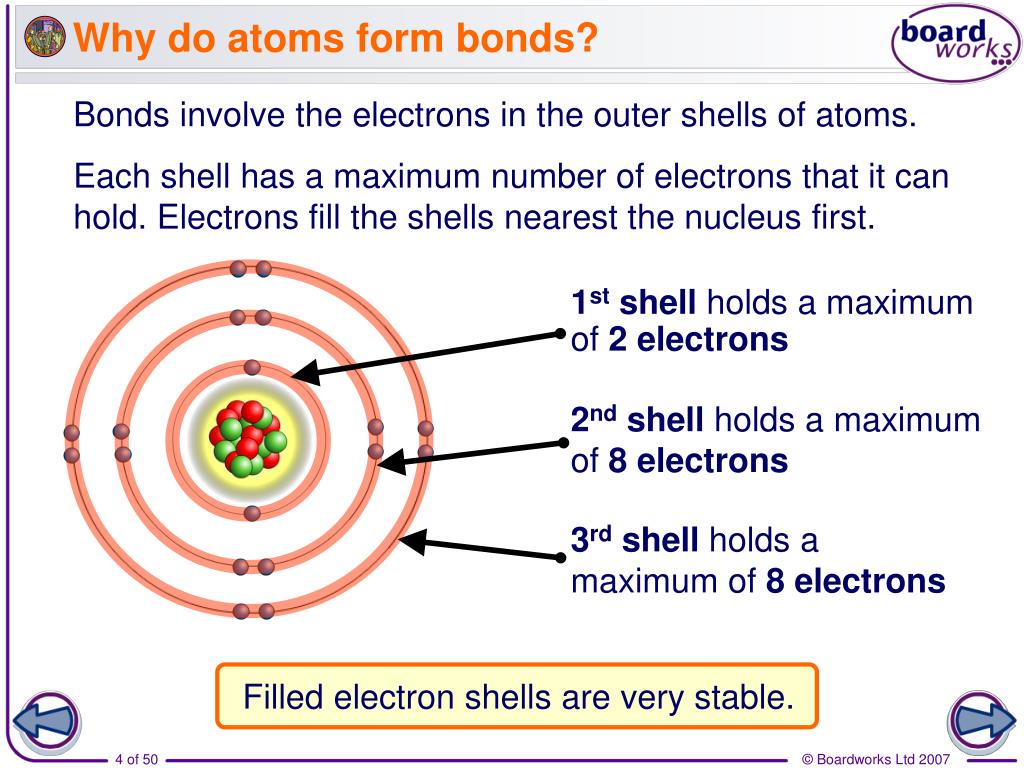
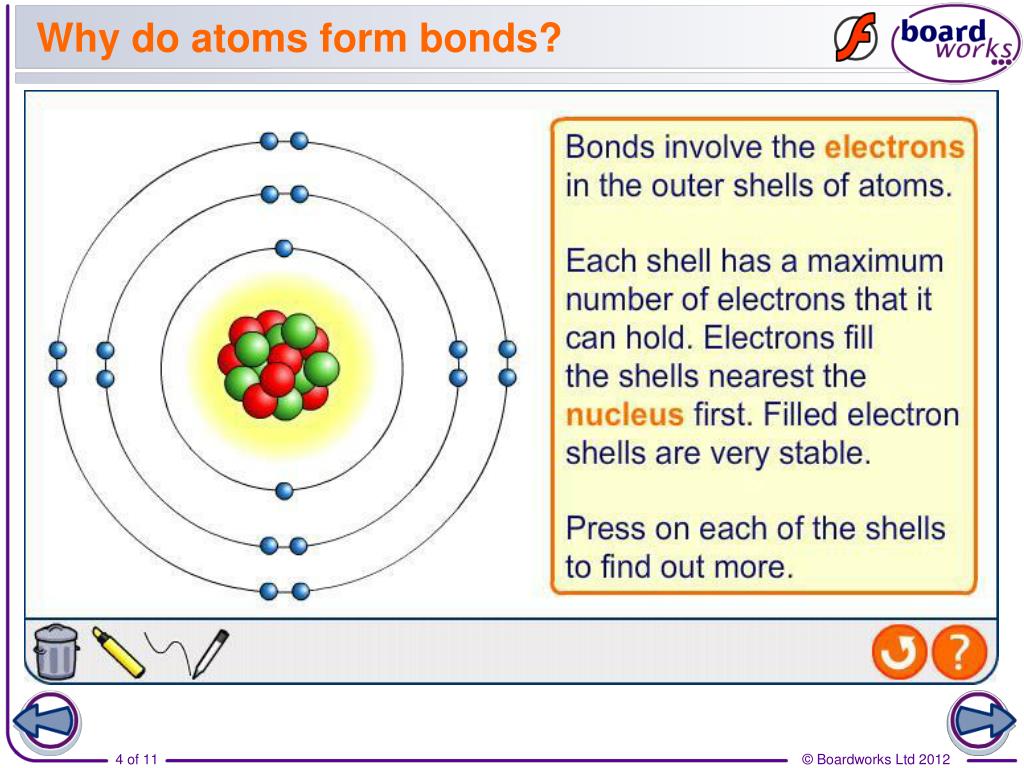
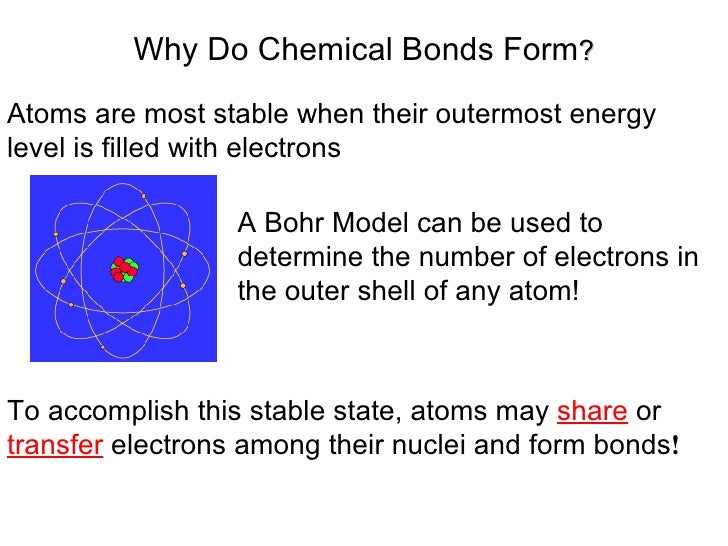
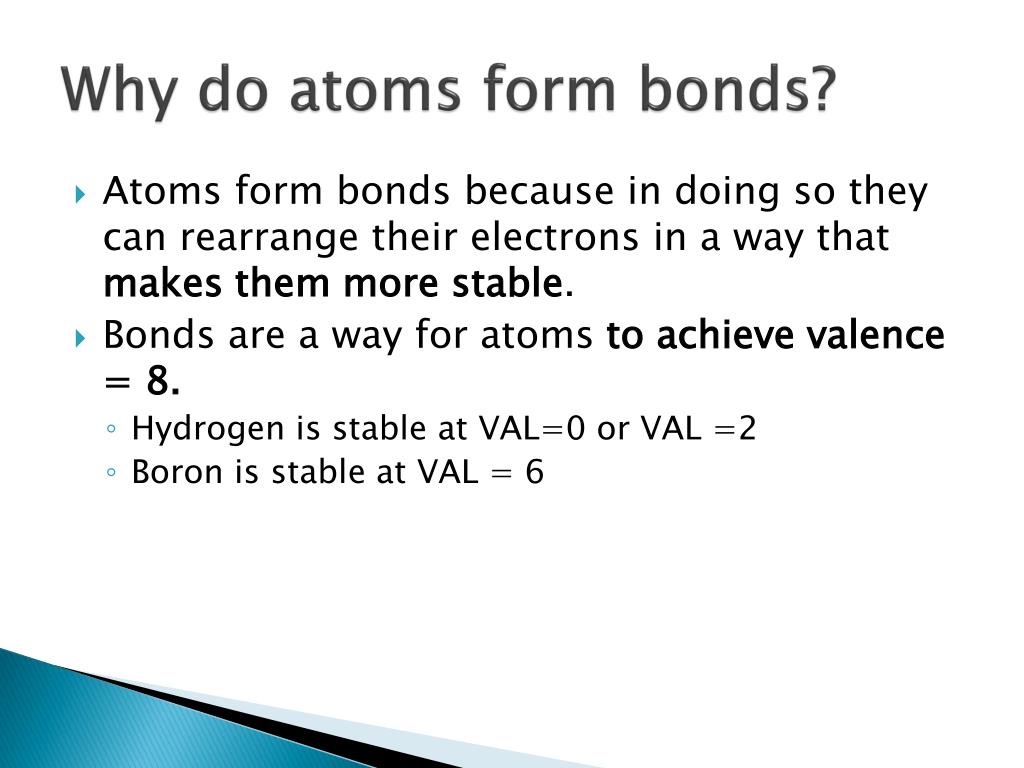
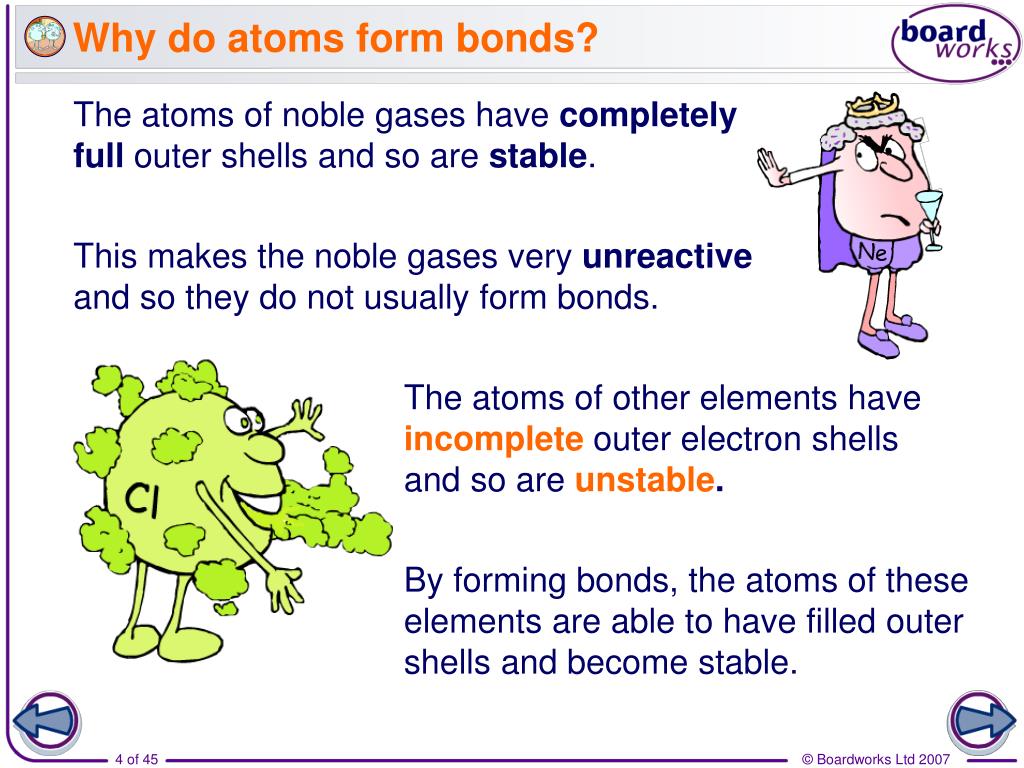
(often used as a synonym for chemical) a compound. Attraction between atoms or ions leads to a chemical bond. Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full outer energy level, which is the most stable arrangement of electrons. According to the types of bonds contained in a molecule, the physical properties including melting point, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity and solubility are determined. 149) why does the octet rule not always refer to a stable arrangement of eight valence electrons? The type of chemical bond maximizes the stability of the atoms that form it. Web sep 4, 2021 3.2: Web why do atoms bond? Web why do atoms form chemical bonds? Web bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons.
Web atoms form chemical bonds to make their outer electron shells more stable. According to the types of bonds contained in a molecule, the physical properties including melting point, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity and solubility are determined. Web why do atoms form chemical bonds? Simply put, atoms form bonds in order to become more stable. At the start of this article, we introduced you to a chemical bond: There are three different types of chemical bonds:. But why do atoms bond to each other in this way? Web a chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules, crystals, and other structures. Web why form chemical bonds? Web chemical bonding, any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other species.
PPT What are bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5980343
Web sep 4, 2021 3.2: 149) why does the octet rule not always refer to a stable arrangement of eight valence electrons? Web posted by city chemical on monday, 01 april 2019. Atoms form chemical bonds because they want a lower energy and more stable electron configuration. Web a chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that.
Why Do Atoms Form Chemical Bond in Urdu Hindi Lecture /Chemistry for
Web sep 4, 2021 3.2: All bonds appear to link atoms through a sharing of — or an attempt to share — electrons. Simply put, atoms form bonds in order to become more stable. Attractive forces between atoms that are strong enough to make the linked elements function as a single unit. Some of the attractive forces are weak, some.
Characteristics of Chemical Bonds 1. To understand why atoms form bonds
Web why form chemical bonds? Many atoms become stable when their valence shell is filled with electrons or when they satisfy the. Web posted by city chemical on monday, 01 april 2019. Atoms form chemical bonds because they want a lower energy and more stable electron configuration. All bonds appear to link atoms through a sharing of — or an.
PPT Ions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6738771
Web why form chemical bonds? Atoms form chemical bonds because they want a lower energy and more stable electron configuration. Many atoms become stable when their valence shell is filled with electrons or when they satisfy the. (often used as a synonym for chemical) a compound. Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full outer energy level, which is the.
Biochemistry Honors
Web why do atoms bond? Many atoms become stable when their valence shell is filled with electrons or when they satisfy the. All bonds appear to link atoms through a sharing of — or an attempt to share — electrons. Web chemical bonding, any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules, ions, crystals, and other.
PPT Chemical Bonding What and Why PowerPoint Presentation, free
Some of the attractive forces are weak, some are very strong. The type of chemical bond maximizes the stability of the atoms that form it. Web sep 4, 2021 3.2: Web why do atoms form chemical bonds? The attraction between different atoms that enables the formation of molecules or compounds.
PPT Atomic structure and chemical bonding PowerPoint Presentation
Web bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web posted by city chemical on monday, 01 april 2019. Some of the attractive forces are weak, some are very strong. Web why do atoms bond? According to the types of bonds contained in a molecule, the physical properties including melting point, hardness, electrical and thermal conductivity and solubility are.
CHEMISTRY 9TH CH 4, LECTURE 1, Why do Atoms Form Chemical Bonds
Web a chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules, crystals, and other structures. 149) why does the octet rule not always refer to a stable arrangement of eight valence electrons? Web why do atoms bond? Many atoms become stable when their valence shell is filled with electrons or when they satisfy.
PPT Chapter 7 Atoms & Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web why do atoms form chemical bonds? Web bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Simply put, atoms form bonds in order to become more stable. Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full outer energy level, which is the most stable arrangement of electrons. 149) why does the octet rule not always refer to a stable arrangement.
PPT Why do atoms form bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
At the start of this article, we introduced you to a chemical bond: Atoms form chemical bonds because they want a lower energy and more stable electron configuration. Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a full outer energy level, which is the most stable arrangement of electrons. According to the types of bonds contained in a molecule, the physical properties.
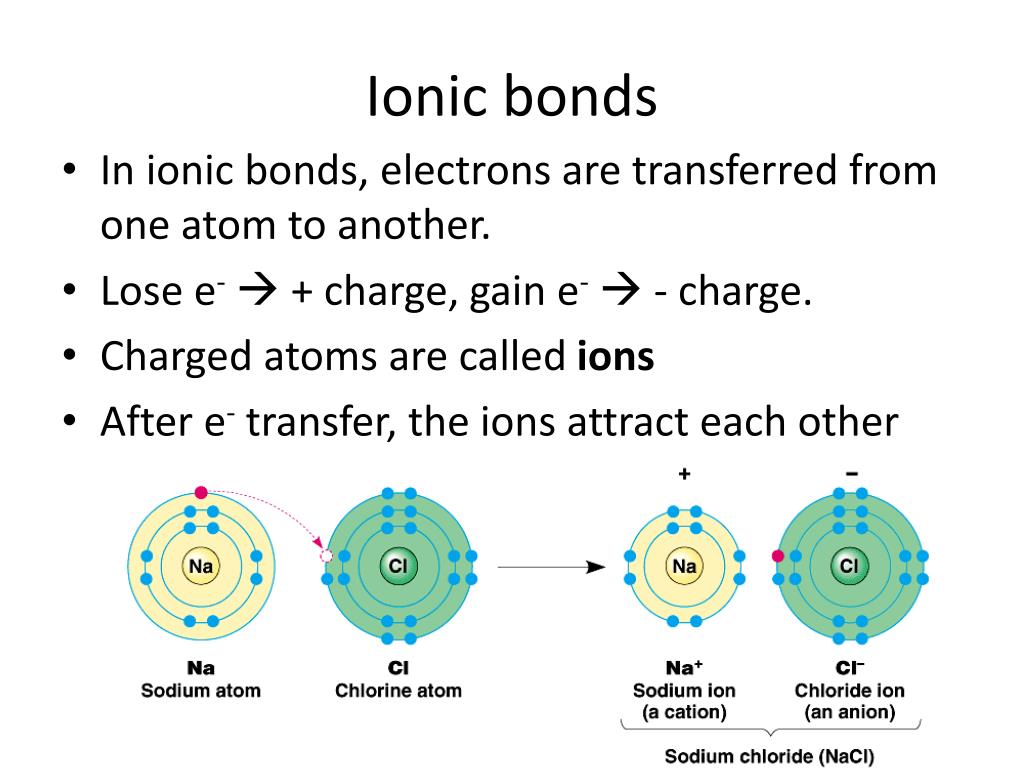
Attraction Between Atoms Or Ions Leads To A Chemical Bond.
But why do atoms bond to each other in this way? The attraction between different atoms that enables the formation of molecules or compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. Web posted by city chemical on monday, 01 april 2019.
Web Bonds Form When Atoms Share Or Transfer Valence Electrons.
Web sep 4, 2021 3.2: Atoms form chemical bonds because they want a lower energy and more stable electron configuration. Web why form chemical bonds? There are three different types of chemical bonds:.
Atoms Form Chemical Bonds To Achieve A Full Outer Energy Level, Which Is The Most Stable Arrangement Of Electrons.
Web why do atoms form chemical bonds? (often used as a synonym for chemical) a compound. When atoms approach one another, their electrons interact and tend to distribute themselves in space so that the total energy is lower than it would be in any alternative arrangement. Web why do atoms bond?
According To The Types Of Bonds Contained In A Molecule, The Physical Properties Including Melting Point, Hardness, Electrical And Thermal Conductivity And Solubility Are Determined.
Some of the attractive forces are weak, some are very strong. Web atoms form chemical bonds to make their outer electron shells more stable. All bonds appear to link atoms through a sharing of — or an attempt to share — electrons. Web a chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules, crystals, and other structures.