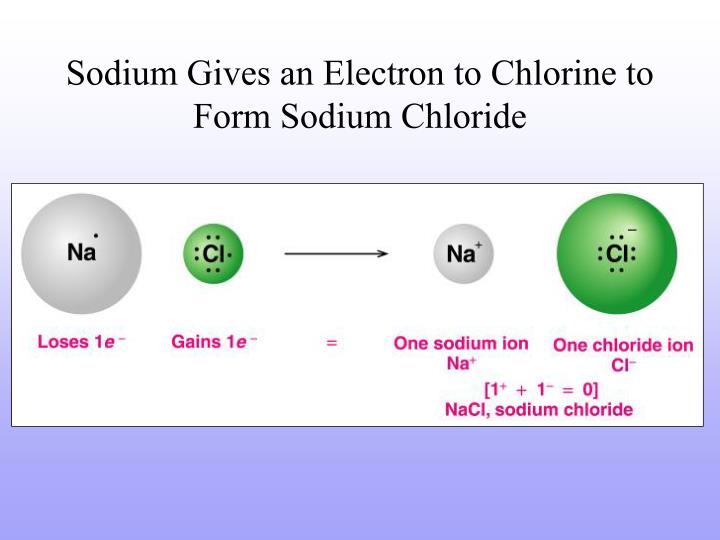
When Sodium Atoms Form Sodium Ions They
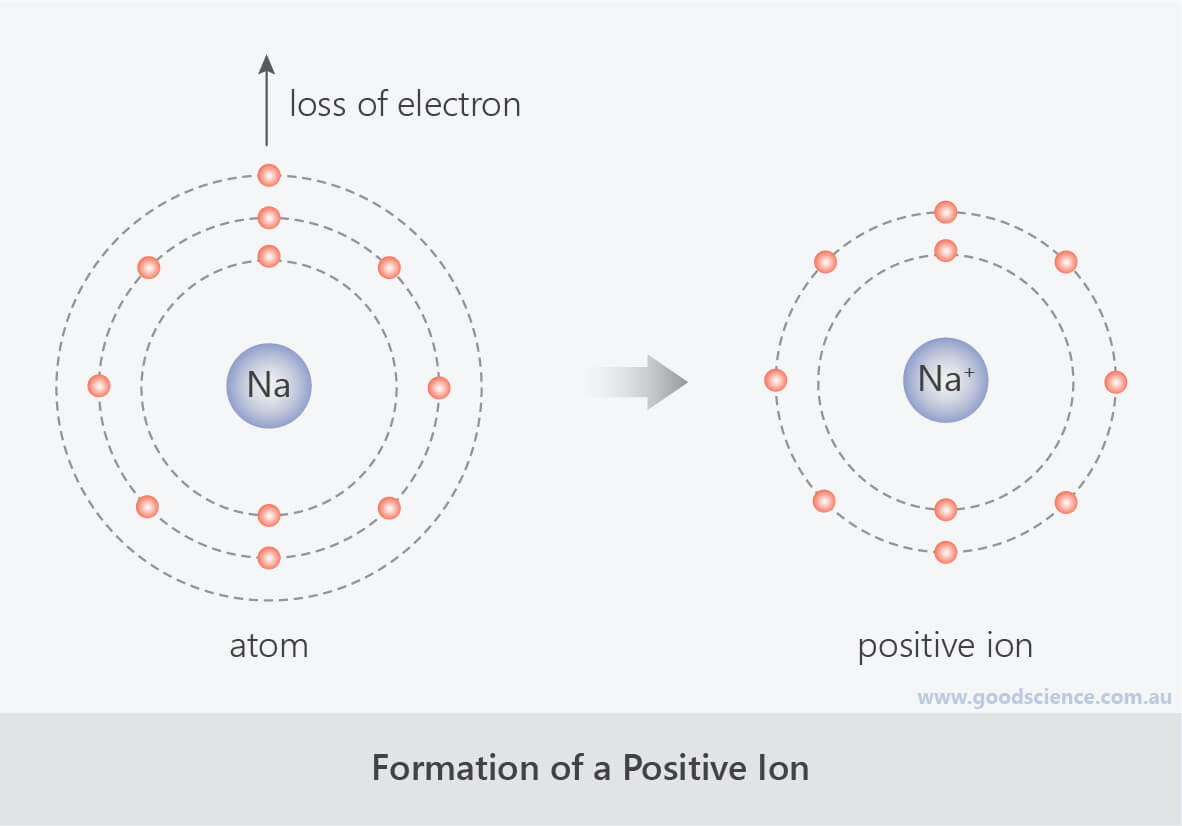
When Sodium Atoms Form Sodium Ions They - Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2 to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. Web a sodium ion is formed when a sodium atom loses a single electron. It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. Compare and contrast a sodium atom and a sodium ion and. Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. Lose electrons any astronomical body that revolves around a larger body is called a. This involves sodium (and its big brother potassium) diffusing through cell membranes. Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. (in chapter 9 “chemical bonds”, we will discuss why atoms form the charges they do.) Sodium diffuses in and is pumped back out, while potassium does the reverse journey.
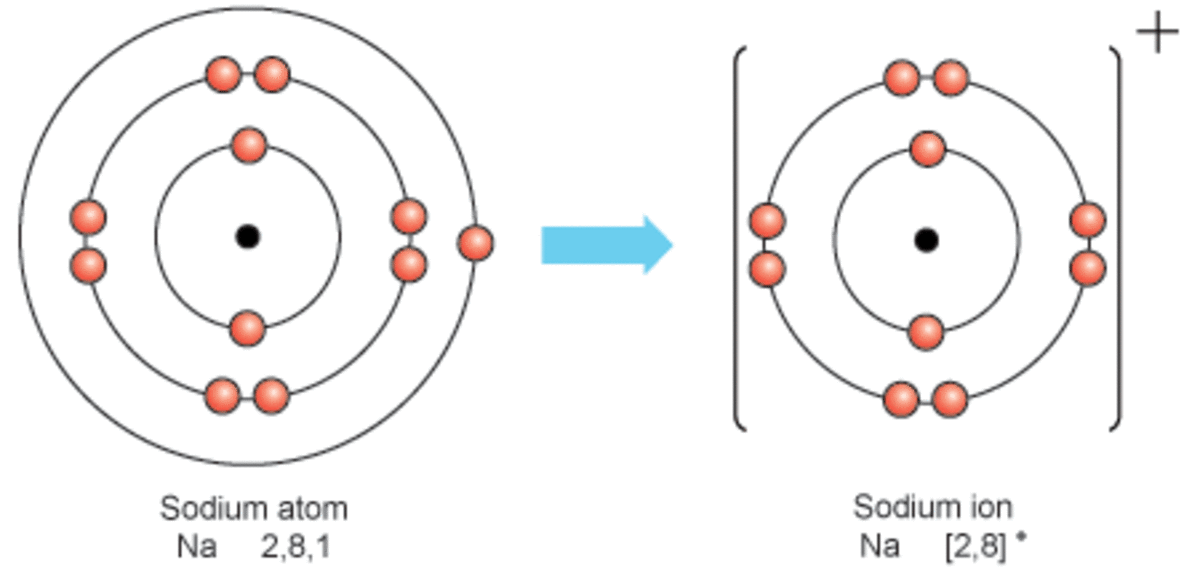
Compare and contrast a sodium atom and a sodium ion and. This involves sodium (and its big brother potassium) diffusing through cell membranes. Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. Thus, if you commit the information in table \(\pageindex{1}\) to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. Web sodium ions are used to build up electrical gradients in the firing of neurons in the brain. The ions formed are negative,. Web the sodium ion, na +, has the electron configuration with an octet of electrons from the second principal energy level. Web when sodium atoms form sodium ions, they a. Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2 to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form.
It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. Web when sodium atoms form sodium ions, they a. Web when sodium atoms form sodium ions, they a. Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2 to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. This involves sodium (and its big brother potassium) diffusing through cell membranes. The term isoelectronic refers to an atom and an ion of a different atom (or two different ions) that have the same electron configuration. (in chapter 9 “chemical bonds”, we will discuss why atoms form the charges they do.) Sodium diffuses in and is pumped back out, while potassium does the reverse journey. Lose electrons any astronomical body that revolves around a larger body is called a. Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust.
Sodium Atom Science Notes and Projects
Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. Web sodium ions are used to build up electrical gradients in the firing of neurons in the brain. The ion is electrically charged, while the atom is electrically neutral. Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2.
PPT Valence Electrons PowerPoint Presentation ID651377
Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Lose electrons any astronomical body that revolves around a larger body is called a. Web the sodium ion, na +, has the electron configuration with an octet of electrons from the second principal energy level. Web a sodium ion.
The top panel of this figure shows the orbit model of a sodium atom and
Lose electrons any astronomical body that revolves around a larger body is called a. Web sodium is a chemical element with the symbol na (from latin natrium) and atomic number 11. This involves sodium (and its big brother potassium) diffusing through cell membranes. It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. Web when sodium atoms form.
3.2 Ions The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
(in chapter 9 “chemical bonds”, we will discuss why atoms form the charges they do.) Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Web sodium ions are used to build up electrical gradients in the firing of neurons in the brain. The ion is electrically charged, while.
How reactive is an atom of Sodium(Na) and why?
Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. Web a sodium ion is formed when a sodium atom loses a single electron. Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2 to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. Lose electrons any astronomical.
化学键原子如何结合?把原子结合在一起的力是什么?——Owlcation 188宝金博官网到底是哪个
Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Compare and contrast a sodium atom and a sodium ion and. (in chapter 9 “chemical bonds”, we will discuss why atoms form the charges they do.) Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table..
Formation of Ions and Ionic Compounds Good Science
Web the sodium ion, na +, has the electron configuration with an octet of electrons from the second principal energy level. The ion is electrically charged, while the atom is electrically neutral. In 1807 sir humphry davy became the first to prepare sodium in its elemental form, applying electrolysis to fused sodium hydroxide (naoh). Web a sodium ion is formed.
Atom sodium Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
Lose electrons any astronomical body that revolves around a larger body is called a. Thus, if you commit the information in table \(\pageindex{1}\) to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. Sodium diffuses in and is pumped back out, while potassium does the reverse journey. Web the sodium ion, na +, has the electron configuration with an.
Ionic Properties
Thus, if you commit the information in table 3.2 to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. Web sodium ions are used to build up electrical gradients in the firing of neurons in the brain..
3d render of atom structure of sodium isolated over white background
Thus, if you commit the information in table \(\pageindex{1}\) to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form. Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. Web the sodium ion, na +, has the electron configuration with an octet of electrons from the second principal.
In 1807 Sir Humphry Davy Became The First To Prepare Sodium In Its Elemental Form, Applying Electrolysis To Fused Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh).
This involves sodium (and its big brother potassium) diffusing through cell membranes. Sodium diffuses in and is pumped back out, while potassium does the reverse journey. Web a sodium ion is formed when a sodium atom loses a single electron. Thus, if you commit the information in table \(\pageindex{1}\) to memory, you will always know what charges most atoms form.
Web When Sodium Atoms Form Sodium Ions, They A.
Web properties and production sir humphry davy because sodium is extremely reactive, it never occurs in the free state in earth’s crust. The ion is electrically charged, while the atom is electrically neutral. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Web when sodium atoms form sodium ions, they a.
Web The Sodium Ion, Na +, Has The Electron Configuration With An Octet Of Electrons From The Second Principal Energy Level.
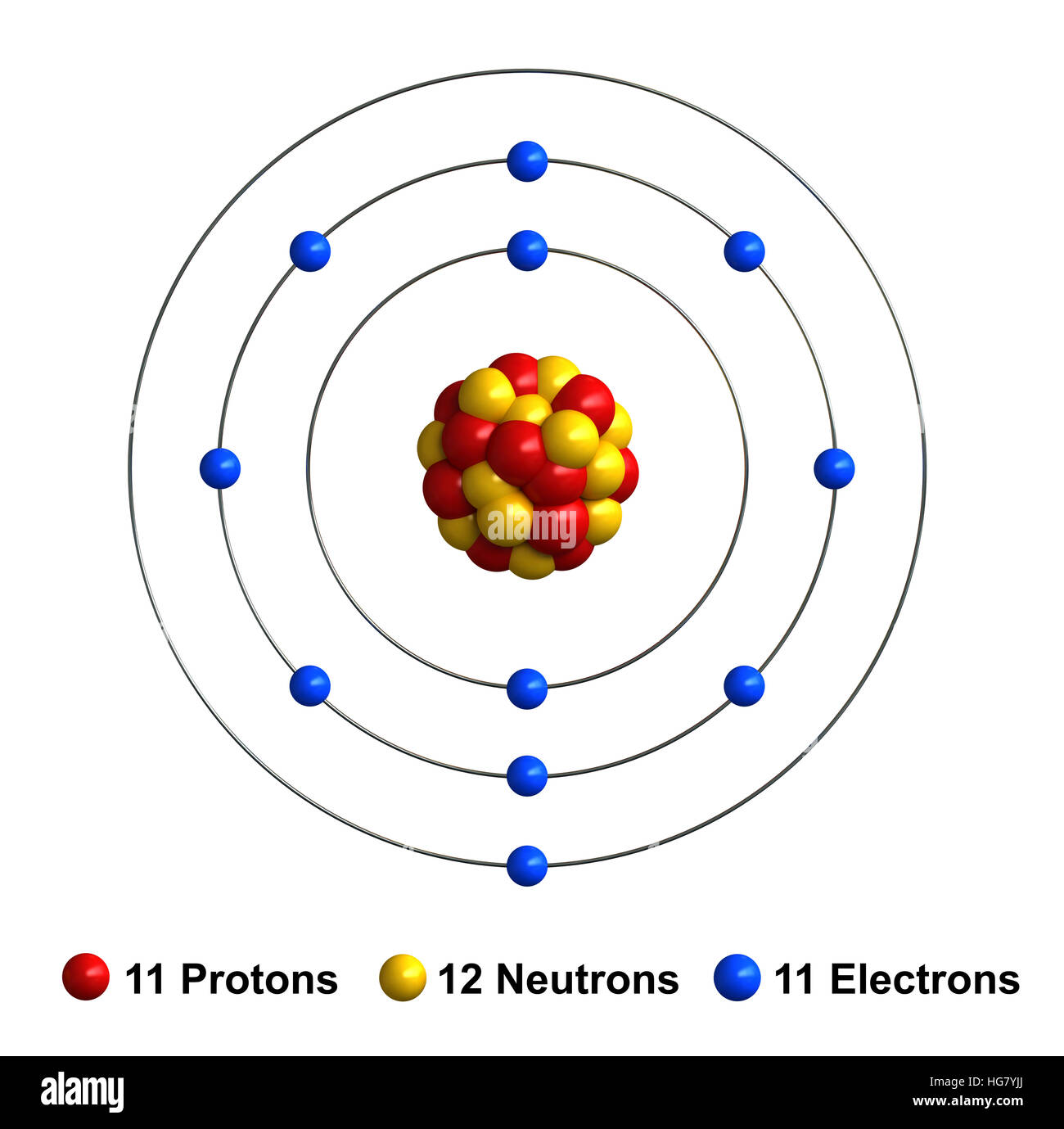
Web sodium is a chemical element with the symbol na (from latin natrium) and atomic number 11. It is now the same as that of the noble gas neon. Compare and contrast a sodium atom and a sodium ion and. Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge.
The Ions Formed Are Negative,.
Its only stable isotope is 23 na. Web when sodium atoms form ions, they always form a 1+ charge, never a 2+ or 3+ or even 1− charge. The term isoelectronic refers to an atom and an ion of a different atom (or two different ions) that have the same electron configuration. (in chapter 9 “chemical bonds”, we will discuss why atoms form the charges they do.)