Ionic Bonds Form Between
Ionic Bonds Form Between - Web condition for ionic bonding. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur. [noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. The two elements or ions. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Web ionic bonds are formed between cations and anions. Web ionic bond definition, the electrostatic bond between two ions formed through the transfer of one or more electrons. Web compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: The following are the conditions for the formation of ionic bonding between chemical substances;
These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ). In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic. In doing so, cations are formed. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic. Web ionic bonds usually occur between metal and nonmetal ions. Web bonds between two nonmetals are generally covalent; Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
Ionic bonding can result from a redox reaction when atoms of an element (usually metal), whose ionization energy is low, give some of their electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Web forming an ionic bond the chemical bond that is formed between 2 2 atoms through the transfer of one or more electrons from the electropositive or metallic. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic. The oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms. Web ionic bonds usually occur between metal and nonmetal ions. Web compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: Web condition for ionic bonding.
10 Notable Differences Between Ionic And Covalent Bonds Current
Web to illustrate further, consider the two major types of chemical bonds: The oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to. Web ionic bond definition, the electrostatic bond between two ions formed through the transfer of one or more electrons. An atom of another element (usually nonmetal) with greater electron affinity accepts one or more electrons to attain a stable electron.
How Does An Ionic Bond Form Between Sodium And Chlorine slideshare
Web to illustrate further, consider the two major types of chemical bonds: So how do you know what kind of bond an atom will make? The two elements or ions. For example, sodium (na), a metal, and chloride (cl), a nonmetal, form an ionic bond to make nacl. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic.
Electronegativity Bond Scale Surfguppy Chemistry made easy for
The two elements or ions. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic. [noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. Web compounds.
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
[noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. The two elements or ions. An atom of another element (usually nonmetal) with greater electron affinity accepts one or more electrons to attain a stable electron configuration, and after accepting ele… Ionic bonding can result from a redox reaction when atoms of an element (usually.
savvychemist Ionic Bonding (2) Dot and cross diagrams/Lewis structures
Web bonds between two nonmetals are generally covalent; Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Web ionic bonds form when two or more ions come together and are held together by charge differences. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic. The oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted to.
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Life Chemistry)
[noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. Web condition for ionic bonding. Ionic bonding can result from a redox reaction when atoms of an element (usually metal), whose ionization energy is low, give some of their electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Web ionic bonds are one of the two main.
Ionic Compounds Ionic bonds, Properties, Formation, Examples, Videos
For example, sodium (na), a metal, and chloride (cl), a nonmetal, form an ionic bond to make nacl. [noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. Web forming an ionic bond the chemical bond that is formed between 2 2 atoms through the transfer of one or more electrons from the electropositive or.
Ionic Properties
Ionic bonding can result from a redox reaction when atoms of an element (usually metal), whose ionization energy is low, give some of their electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Electrostatic forces of attraction between. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely.
Examples of Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ). Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron(s).
Ionic Bond Definition, Types, Properties & Examples
For example, sodium (na), a metal, and chloride (cl), a nonmetal, form an ionic bond to make nacl. [noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms. Web ionic bonds are one of the two.
Covalent Bonds And Ionic Bonds.
Web condition for ionic bonding. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. These oppositely charged ions attract each other to form ionic networks (or lattices ). Web ionic bonds form between two or more atoms by the transfer of one or more electrons between atoms.
Ionic Bonding Can Result From A Redox Reaction When Atoms Of An Element (Usually Metal), Whose Ionization Energy Is Low, Give Some Of Their Electrons To Achieve A Stable Electron Configuration.
Web ionic bonds are one of the two main types of chemical bonds. Electrostatic forces of attraction between. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms and is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
Web Compounds Composed Of Ions Are Called Ionic Compounds (Or Salts), And Their Constituent Ions Are Held Together By Ionic Bonds:
Web ionic bonds form when two or more ions come together and are held together by charge differences. Web ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms. Web ionic bonds usually occur between metal and nonmetal ions. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic.
Web Ionic Bond Definition, The Electrostatic Bond Between Two Ions Formed Through The Transfer Of One Or More Electrons.
Electron transfer produces negative ions called anions and positive ions. They form as a result of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions and usually occur. [noun] a chemical bond formed between oppositely charged species because of their mutual electrostatic attraction. So how do you know what kind of bond an atom will make?

.PNG)
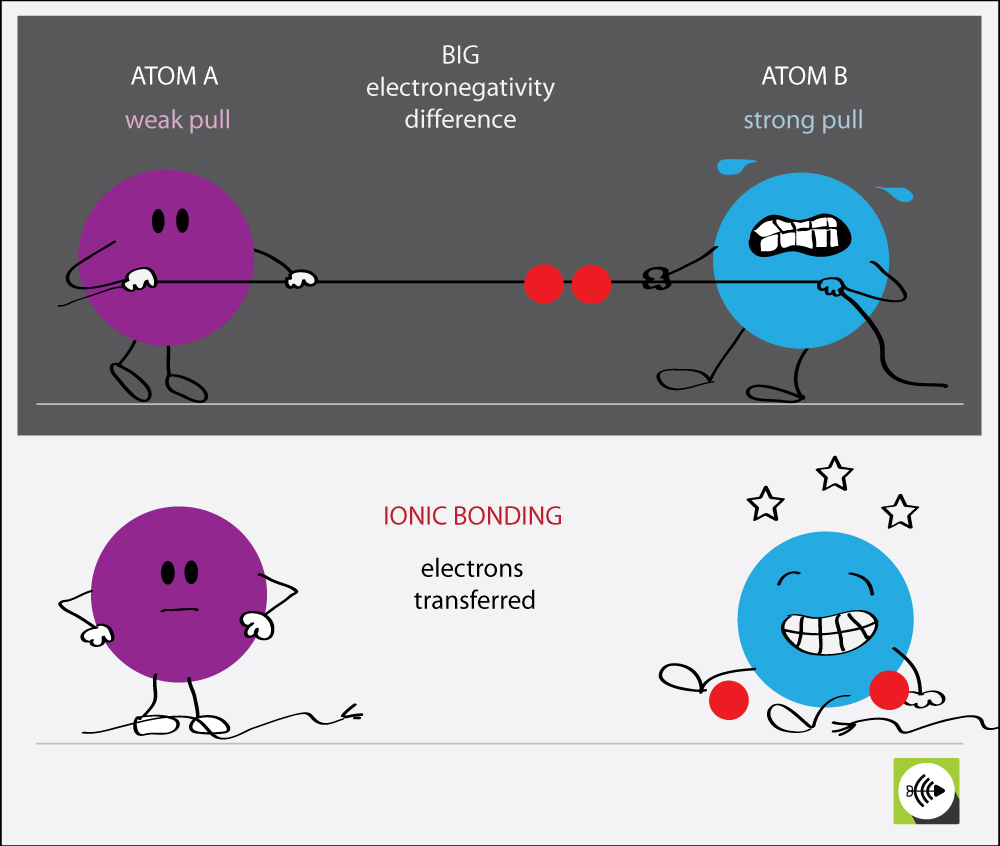

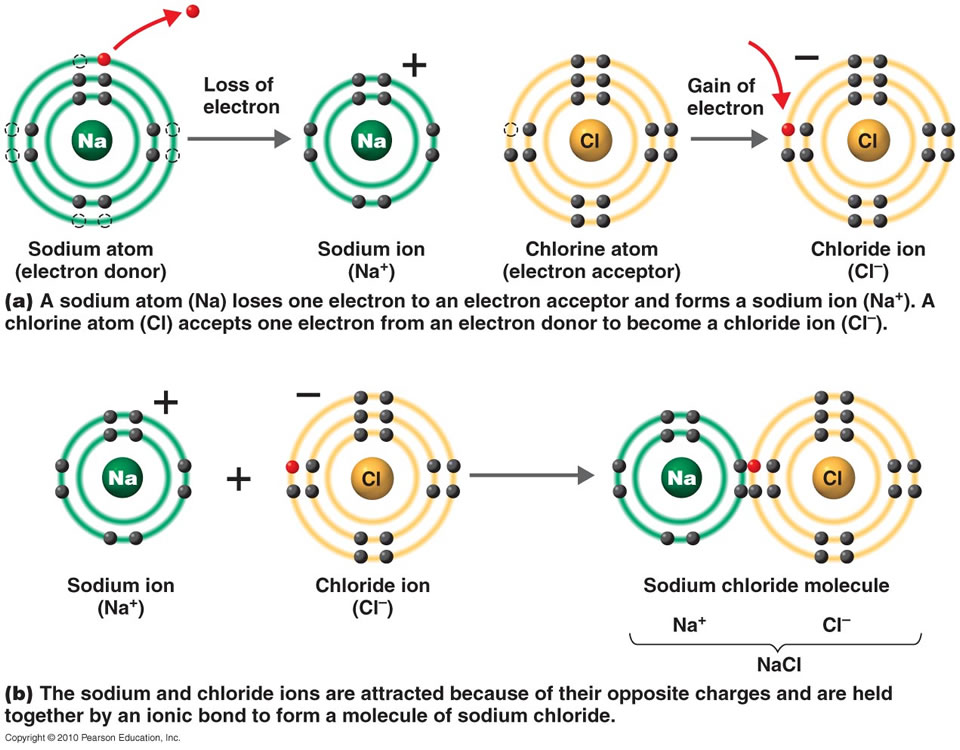

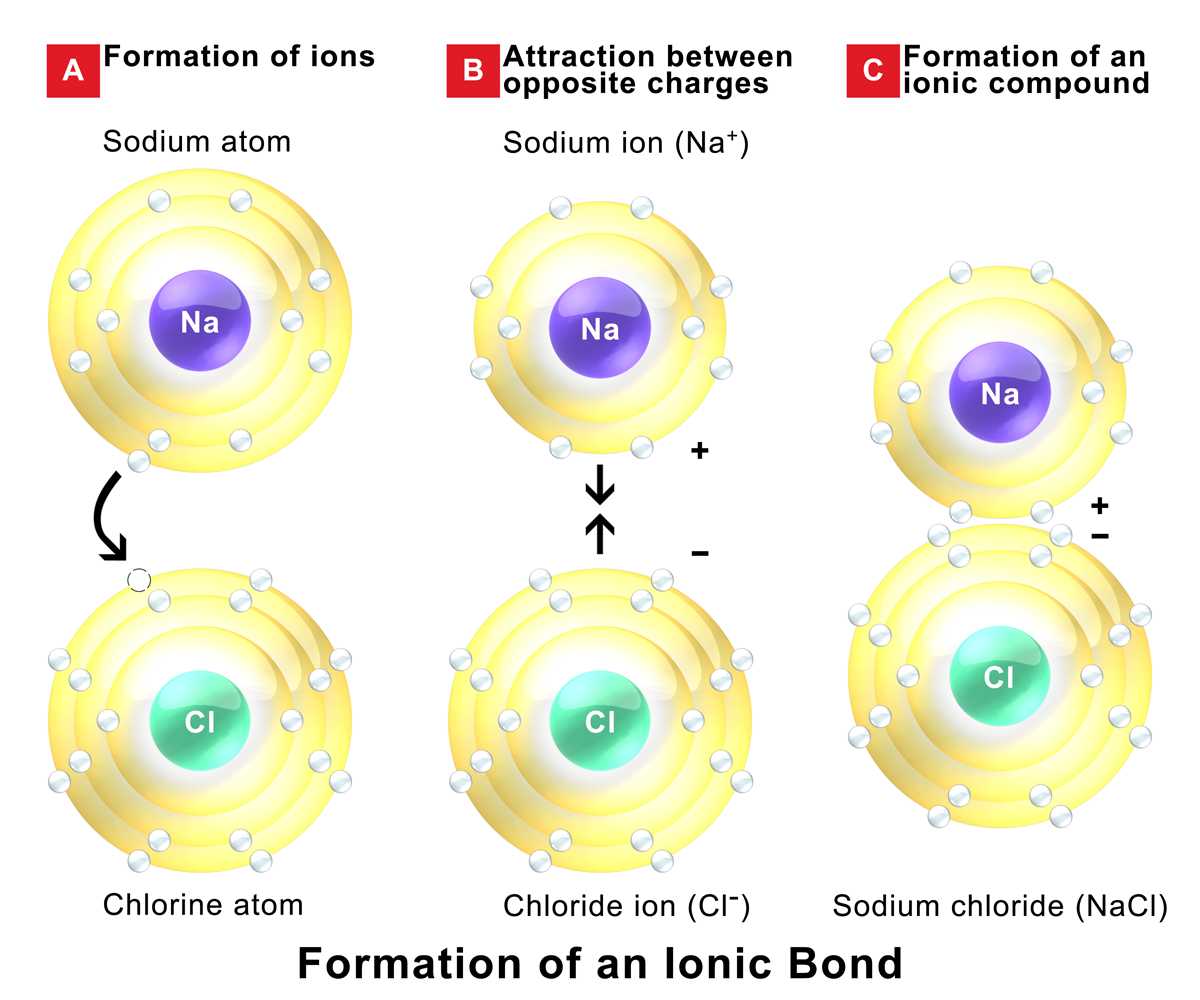

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ionic-bond-58fd4ea73df78ca1590682ad.jpg)
