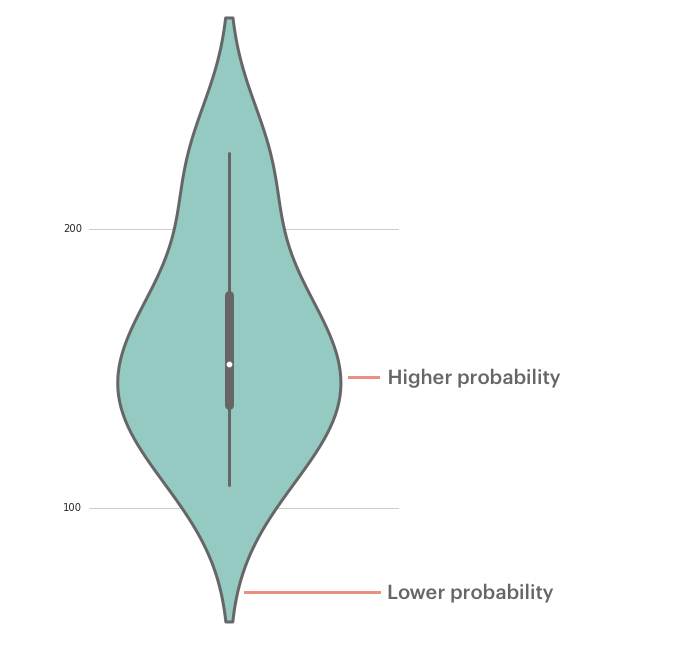
How To Read Violin Plots
How To Read Violin Plots - Web in order to create a violin plot, we just use the violinplot () function in seaborn. In contrast to a box plot, which can only provide summary statistics, violin plots. We can pass in just the x variable and the. It shows the distribution of quantitative data across several levels of one (or more) categorical variables such that those distributions can be compared. We’ll be using the gapminder dataset. Web a violin plot is a mirrored density plot displayed in the same way as a boxplot, but with a different shape. Web there are two main types of violin plots: Web violin plot with plotly express¶ a violin plot is a statistical representation of numerical data. Chartio has a great description for how histograms, kernel density plots, and violin plots are related to each other, including a great description of how kernel density plots. We can use the plot() function to create a plot of the violin data.
Web here are the notes, starting from the bottom number. When to use a violin plot; We’ll start by importing the libraries we need, which include pandas and matplotlib:. We can pass in just the x variable and the. A violin plot is a combination of a box plot and a kernel. Web violin plot with plotly express¶ a violin plot is a statistical representation of numerical data. We’ll be using the gapminder dataset. You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them. How to interpret your plot Web a violin plot plays a similar role as a box and whisker plot.
Chartio has a great description for how histograms, kernel density plots, and violin plots are related to each other, including a great description of how kernel density plots. Web a violin plot is a mirrored density plot displayed in the same way as a boxplot, but with a different shape. The following code creates a new plot, and then calls plot. Web when you have a numeric response and a categorical grouping variable, violin plots are an excellent choice for displaying the variation with and between your groups of data. A violin plot is a combination of a box plot and a kernel. We can pass in just the x variable and the. A violin plot is just a histogram (or more often a smoothed variant like a kernel density) turned on its side and mirrored. We pass in the dataframe as well as the variables we want to visualize. Web in this guide, you learned how to use the seaborn violinplot () function to create informative violin plots in seaborn. Any textbook that teaches you how to interpret histograms should give you.
Understanding Violin Plots YouTube
Web a violin plot plays a similar role as a box and whisker plot. How to superimpose data on your violin plot; Web here are the notes, starting from the bottom number. We can pass in just the x variable and the. We can use the plot() function to create a plot of the violin data.
How to interpret and create violin plots YouTube
Alternatives to violin plots for visualizing distributions include histograms, box plots, ecdf plots and strip charts. The following code creates a new plot, and then calls plot. It's used to show how numerical data is distributed. It shows the distribution of quantitative data across several levels of one (or more) categorical variables such that those distributions can be compared. Web.
5 reasons you should use a violin graph BioTuring's Blog
You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them. Any textbook that teaches you how to interpret histograms should give you. In contrast to a box plot, which can only provide summary statistics, violin plots. Web a violin plot plays a similar role as a box and whisker plot. A violin plot is a.
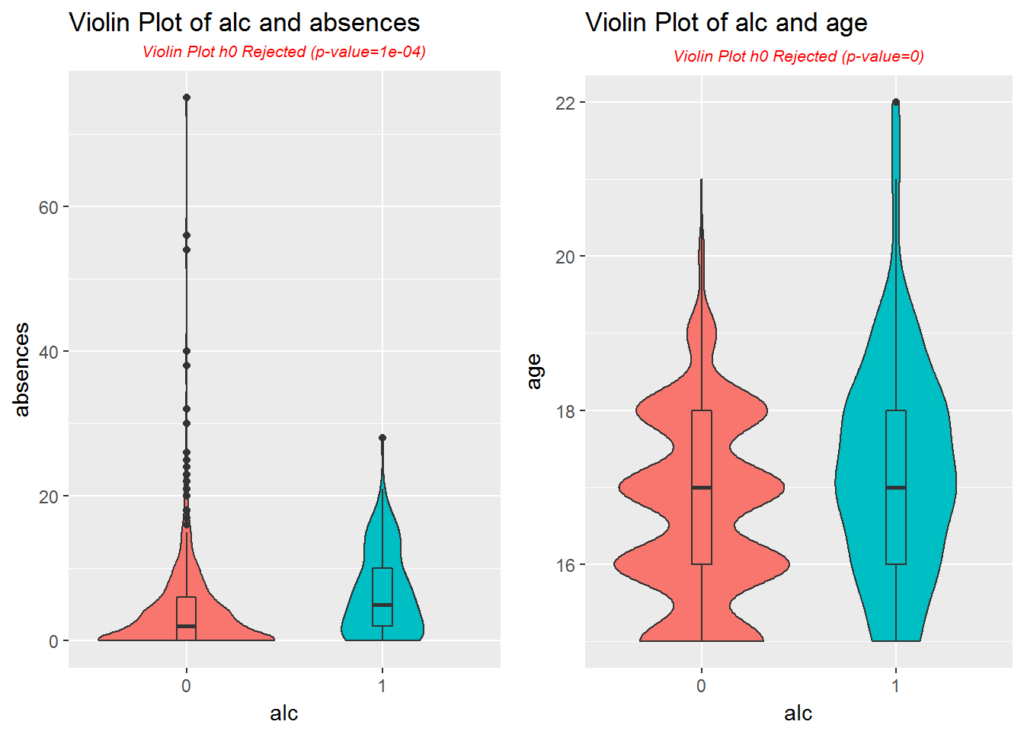
Data Exploratory Analysis Student Alcohol Consumption JustInsighting
It's used to show how numerical data is distributed. How to superimpose data on your violin plot; Web when you have a numeric response and a categorical grouping variable, violin plots are an excellent choice for displaying the variation with and between your groups of data. Before we can create a violin plot, we will need some data to plot..
scrnaseq Interpretation of the violin plots from scRNAseq
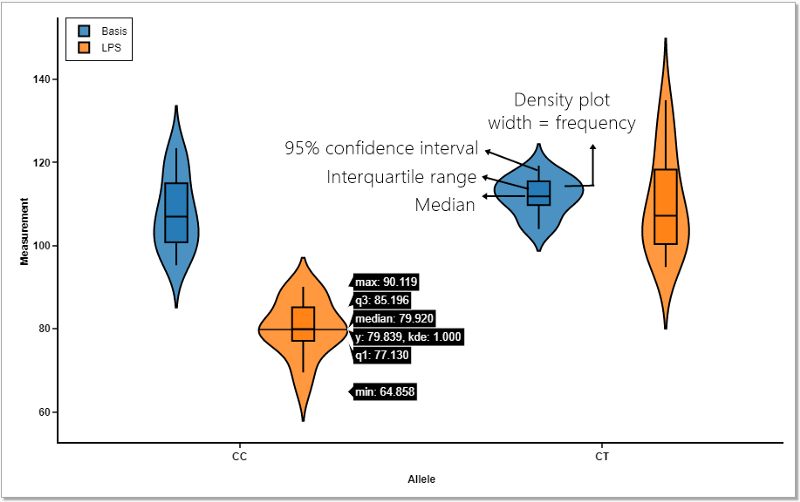
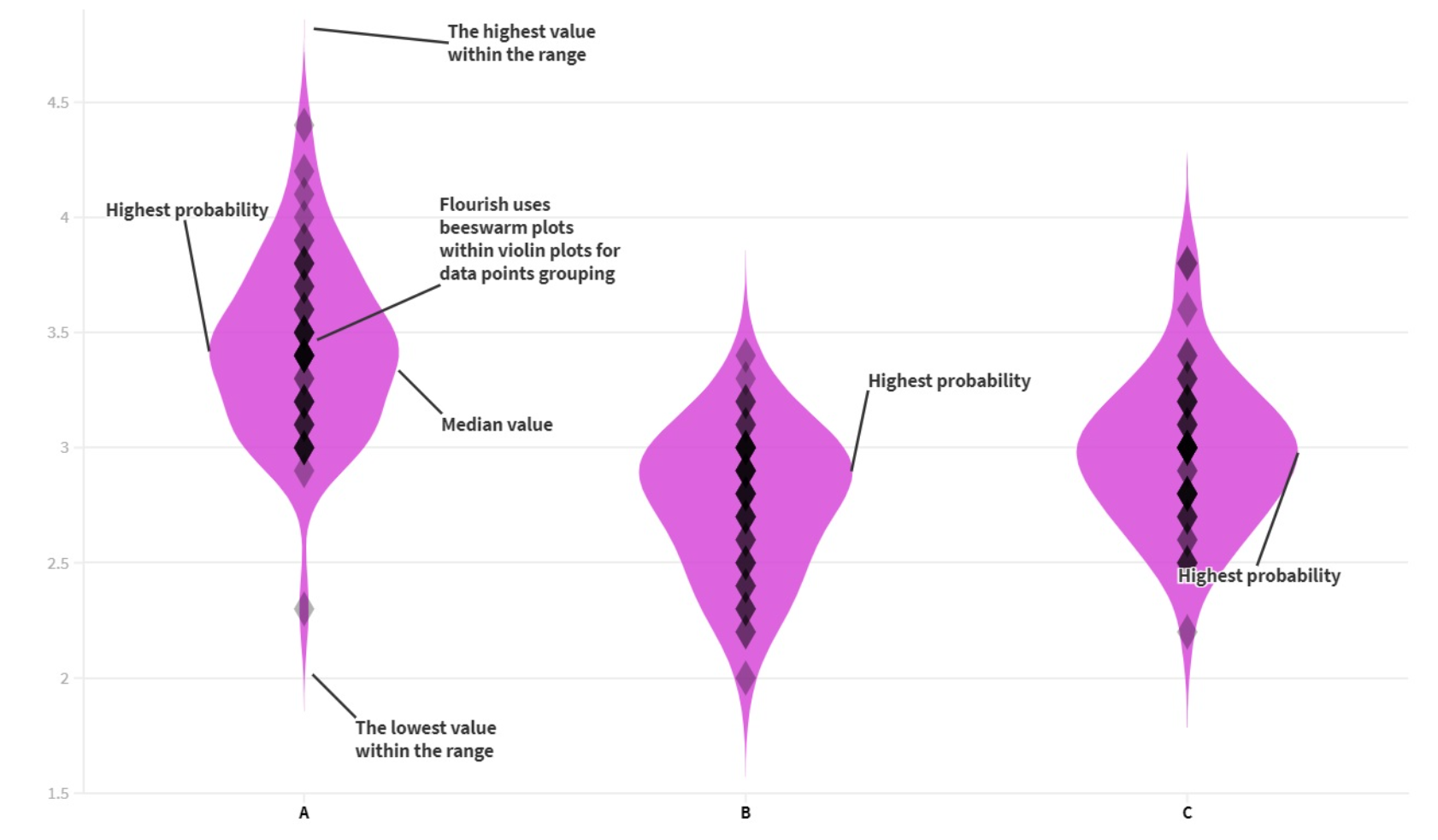
The curve of the violin is limited by the minimum and maximum values in the data set. A violin plot is a combination of a box plot and a kernel. You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them. A violin plot is just a histogram (or more often a smoothed variant like a.
The Violin Plot Actuarial News
When to use a violin plot; Web a violin plot plays a similar role as a box and whisker plot. Web this tutorial will help you interpret a violin plot using the seaborn library. It's used to show how numerical data is distributed. How to superimpose data on your violin plot;
Violin Plots 101 Visualizing Distribution and Probability Density Mode
The curve of the violin is limited by the minimum and maximum values in the data set. Web a violin plot is a mirrored density plot displayed in the same way as a boxplot, but with a different shape. It shows the distribution of quantitative data across several levels of one (or more) categorical variables such that those distributions can.
14 Explanation of Violin plot. Densities are estimated using a
We can pass in just the x variable and the. You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them. Web there are two main types of violin plots: Web these violin outlines can be read like a kernel density plot, which you can read kinda like a histogram. It shows the distribution of quantitative.
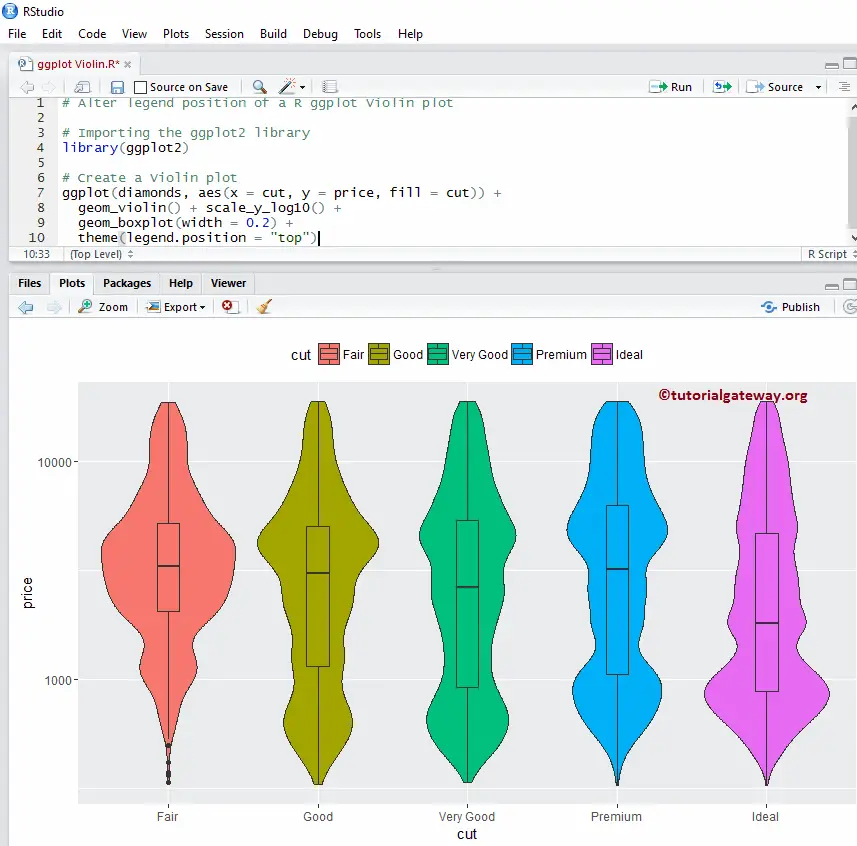
R ggplot2 Violin Plot
Web before diving into creating combined violin and box plots, it is essential to understand the basics of both plot types. Chartio has a great description for how histograms, kernel density plots, and violin plots are related to each other, including a great description of how kernel density plots. Web there are two main types of violin plots: Alternatives to.
Violin Plots 101 Visualizing Distribution and Probability Density Mode
We can pass in just the x variable and the. Web these violin outlines can be read like a kernel density plot, which you can read kinda like a histogram. We’ll start by importing the libraries we need, which include pandas and matplotlib:. You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them. A violin.
Web When You Have A Numeric Response And A Categorical Grouping Variable, Violin Plots Are An Excellent Choice For Displaying The Variation With And Between Your Groups Of Data.
Web these violin outlines can be read like a kernel density plot, which you can read kinda like a histogram. Web here are the notes, starting from the bottom number. Before we can create a violin plot, we will need some data to plot. It is similar to a box plot, with the addition of a rotated kernel density plot on each side.
When To Use A Violin Plot;
Alternatives to violin plots for visualizing distributions include histograms, box plots, ecdf plots and strip charts. A violin plot is a combination of a box plot and a kernel. Web this tutorial will help you interpret a violin plot using the seaborn library. We pass in the dataframe as well as the variables we want to visualize.
The Following Code Creates A New Plot, And Then Calls Plot.
The curve of the violin is limited by the minimum and maximum values in the data set. Any textbook that teaches you how to interpret histograms should give you. We can use the plot() function to create a plot of the violin data. You first learned what violin plots are and when you may want to use them.
Web A Violin Plot Plays A Similar Role As A Box And Whisker Plot.
How to interpret your plot It shows the distribution of quantitative data across several levels of one (or more) categorical variables such that those distributions can be compared. We can pass in just the x variable and the. Web there are two main types of violin plots: